SPRIselect Bead-Based Reagent
Applications: DNA Size Selection, PCR Purification, NGS Cleanup
Suggested in over 40 NGS library preparation kits, the SPRIselect reagent provides flexibility and control over the DNA size selection process with minimal lot-to-lot variance. Plus, it's stable at room temperature.
Order SPRIselect Reagent Right Away
Explore SPRIselect Reagents
We're Better Together: Become an OEM Partner. Learn More →
Overview
The SPRIselect bead-based reagent is designed to provide scientists with more control over the size selection step during NGS library preparation, which is critical for generating high-quality sequencing data. It is powered by proven SPRI technology, which uses paramagnetic beads to selectively bind nucleic acids by type and size.
![]()
Works with fragmented DNA
![]()
Tunable from 150 to 800 bp to offer easy adjustments for specific applications and sequencers
![]()
Eliminates the needs for gels, chips or special instrumentation
![]()
High level of predictability and consistency between different runs and reagent lots
The simplified workflow and automation capability of SPRIselect reagents make the process of size selection more streamlined and less prone to errors, resulting in faster and more reliable sequencing results.
Specifications
| Nucleic Acid Input | Fragmented DNA, PCR products |
| Output | Size Selected DNA |
| Range of Size Selection | 150–800 bp |
| Bead Ratio | Size Selection: Depends on selection point(s); Cleanup: 1.8X. Learn more → |
| Format | Liquid |
| Volumes | 5 mL, 60 mL, or 450 mL |
| Applications | DNA Size Selection, PCR Purification, NGS Cleanup |
| Processing mode | Automated or manual |
| Technology | SPRI paramagnetic bead-based technology |
| Storage | Room Temperature |
Data and Performance
Two different size selections were performed on sheared gDNA from E. coli using SPRIselect reagent. Triplicates were performed per size selection. Each of the triplicates show very consistent size selection capabilities. (Left) Bind to sample ratio of 0.5X for left side size selection. (Right) Bind to sample ratio of 0.5X for right side size selection. DNA size was measured using an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer high sensitivity chip. The peaks at 43 and 115 are internal markers.


Workflows and Protocol
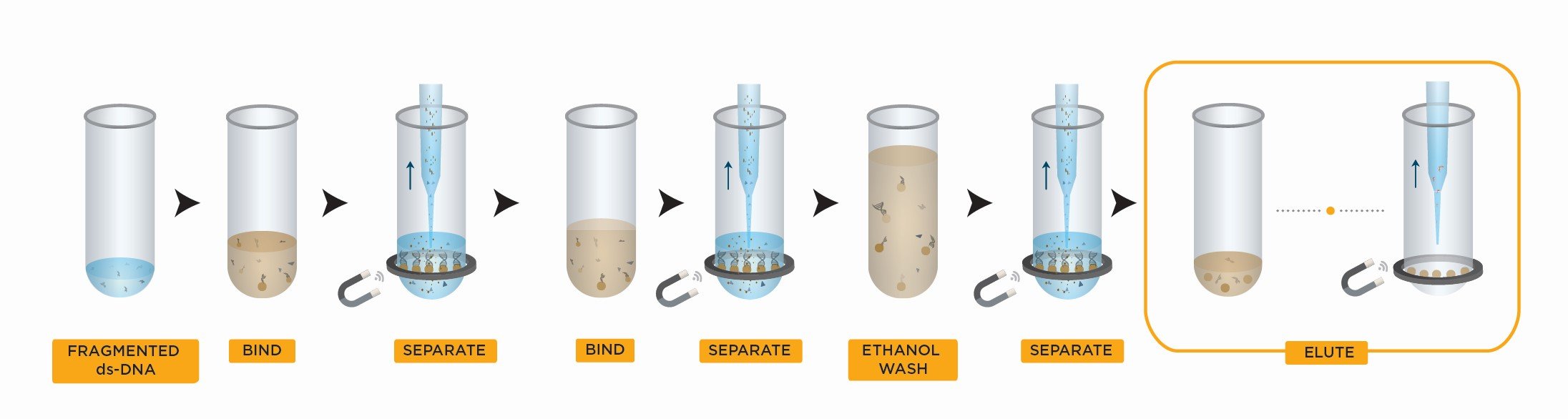
SPRIselect Left Side Size Selection Workflow
- Bind DNA to magnetic beads
- Separate beads from contaminants
- Wash magnetic beads with 85% ethanol to remove contaminants
- Elute DNA from magnetic beads
- Transfer to new plate
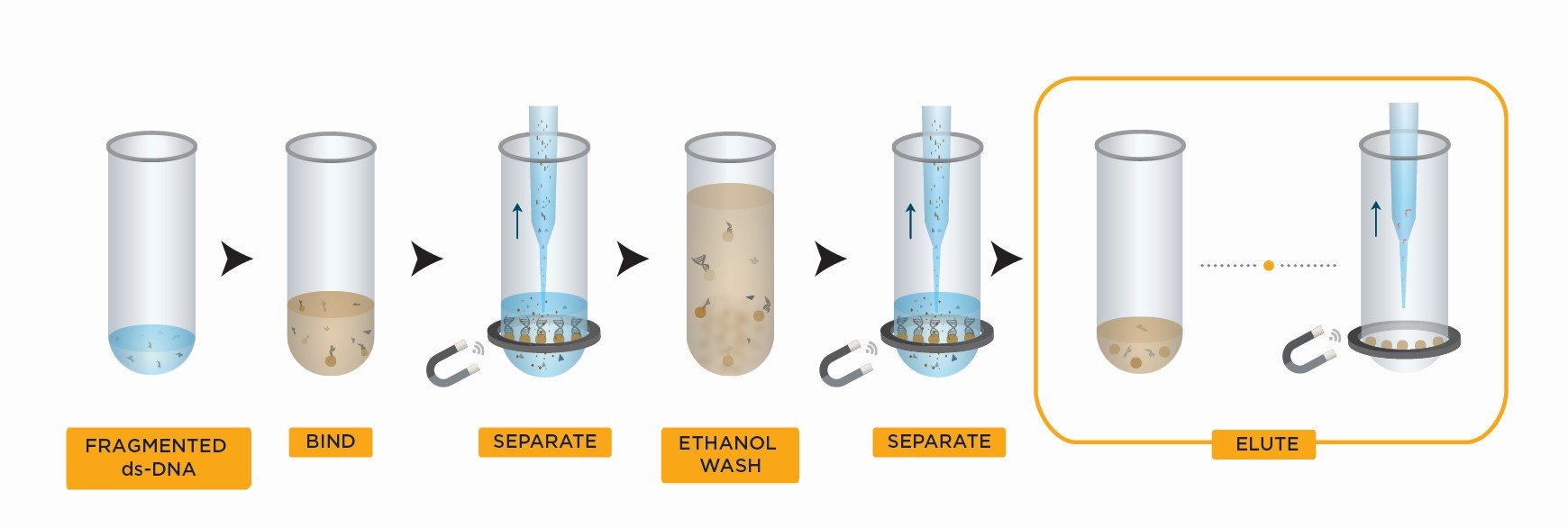
SPRIselect Right Side Size Selection Workflow
- Bind DNA to magnetic beads
- Transfer supernatant to a new plate
- Bind DNA to magnetic beads
- Separate beads from contaminants
- Wash magnetic beads with 85% ethanol to remove contaminants
- Elute DNA from magnetic beads
- Transfer to new plate
SPRIselect bead-based reagent can be performed either manually or automated on a liquid handling system depending on batch size or overall throughput.
In the table you can see estimated hands-on time and total time, in minutes, required to perform 8, 24, 48 and 96 DNA size selections on the Biomek i7 Hybrid Workstation using SPRIselect reagent.
To learn more about automating DNA size selection on the Biomek i-Series Workstations, read our application note.
| Manual Workflow | Automated Workflow | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch Size | 8 | Hands-on Time | 10 | 10 |
| Total Time | 20 | 40 | ||
| 24 | Hands-on Time | 15 | 10 | |
| Total Time | 25 | 42 | ||
| 48 | Hands-on time | NR | 15 | |
| Total Time | NR | 51 | ||
| 96 | Hands-on time | NR | 15 | |
| Total Time | NR | 60 | ||
NR = Not Recommended
Frequently Asked Questions
The main difference between the reagents is the intended use. The SPRIselect reagents are designed and validated for accurate and consistent DNA size selection from lot to lot, while the AMPure XP reagents are primarily validated for PCR purification and NGS cleanup. Read more about the differences here.
We cannot guarantee post-thaw suitability or stability for every application.
No. Any beads carried over to the final destination plate are inert in downstream enzymatic reactions.
We recommend 40 μL. The beads should be submerged when they are in the elution buffer, otherwise when you transfer the eluate to another plate, you may get excessive bead carryover or low yield. In most 96 well PCR plates, it takes 40 μL to cover the beads. Certain combinations of third-party labware and magnetic separation plates may allow for lower elution volumes.
Our beads rely upon a multifactorial equilibrium chemistry for binding, washing, and elution. Binding buffer components facilitate nucleic acid immobilization at functional-group-rich binding sites on the beads and the wash steps preserve this delicate equilibrium while solubilizing contaminants to allow for their removal. Elution disrupts this balance and re-solubilizes nucleic acids to allow for their separation from the beads.
Learn More →
Recovery will vary based on the range of fragment sizes selected and is heavily dependent on the input sample. In general, as specificity increases (and the fragment size range selected narrows) yield will also decrease.
Find Beckman Coulter Life Sciences SPRIselect technical documents here.
Didn't find an answer to your question? Talk to our expert.
Citations
SPRIselect reagents have been cited in over 3,000 publications on Google Scholar and referenced in articles in Science, Nature, and PNAS. Here are three featured articles:
Greenwald WW et al. Subtle changes in chromatin loop contact propensity are associated with differential gene regulation and expression. Nat Commun. 2019 Mar 5;10(1):1054. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08940-5.
Kubo M et al. Single-cell transcriptome analysis of Physcomitrella leaf cells during reprogramming using microcapillary manipulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 May 21;47(9):4539-4553. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz181.
Behera V et al. Interrogating Histone Acetylation and BRD4 as Mitotic Bookmarks of Transcription. Cell Rep . 2019 Apr 9;27(2):400-415.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.03.057.
Technical Documents
Products and demonstrated applications are not intended or validated for use in diagnostic procedures.